Cannabinoids In The Treatment Of Cancer
Cannabinoids are currently used in cancer patients to alleviate wasting, vomiting, nausea, and pain that often accompany cancer. A significant advancement in cannabinoid use in cancer treatment came from the discovery of a potential utility of these, compounds for targeting and killing cancer cells. In 1975 Munson et al. demonstrated that the administration of Δ9-THC, Δ8-THC and cannabinol inhibited the growth of Lewis lung adenocarcinoma cells in vitro as well as in vivo after oral administration in mice. The interest in anticarcinogenic properties of cannabinoids was even renewed after the discovery of the eCB system and the cloning of the specific cannabinoid receptors.
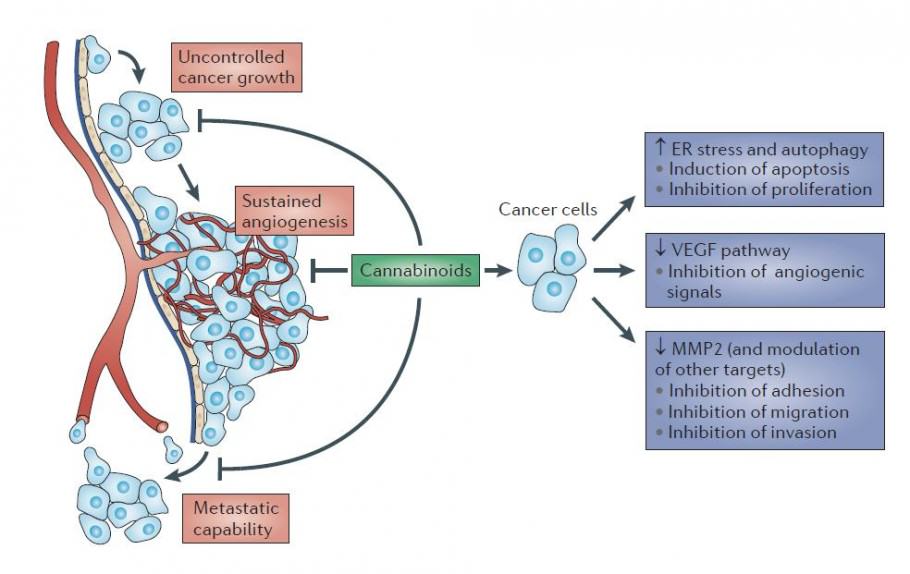
Since then, several cannabinoids have been shown to exert anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects in various cancer types (lung, glioma, thyroid, lymphoma, skin, pancreas, uterus, breast, prostate and colorectal carcinoma) both in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, other antitumourigenic mechanisms of cannabinoids are currently emerging, showing their ability to interfere with tumour neovascularization, cancer cell migration, adhesion, invasion and metastasization.
However, the clinical use of Δ9-THC and additional synthetic agonists is often limited by their unwanted psychoactive side effects, and for this reason interest in non-psychoactive phytocannabinoids, such as CBD, has substantially increased in recent years. Interestingly CBD has no psychotropic activity and, although it has very low affinity for both CB1 and CB2 receptors, it has been recently reported to act with unexpectedly high potency in vitro as antagonist of CB1 receptors in the mouse vas deferens and brain tissues. Additionally, CBD displays inverse agonism at human CB2 receptors. Moreover, other putative molecular targets of CBD are TRPV, 5-HT1A, GPR55 and PPARγ receptors. Besides its beneficial effects in the treatment of pain and spasticity and other CNS pathologies, several reports demonstrated that CBD possesses antiproliferative, pro-apoptotic effects and inhibits cancer cell migration, adhesion and invasion.
⇒ Brain Cancer
A brain tumor or intracranial neoplasm occurs when abnormal cells form within the brain. There are two main types of tumors: malignant or cancerous tumors and benign tumors. Cancerous tumors can be divided into primary tumors that started within the brain and those that spread from somewhere else known as brain metastasis tumors.
⇒ Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the development of cancer from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, fluid coming from the nipple, or a red scaly patch of skin. Breast cancer is a malignant tumor that starts in the cells of the breast. A malignant tumor is a group of cancer cells that can grow into (invade) surrounding tissues or spread (metastasize) to distant areas of the body. The disease occurs almost entirely in women, but men can get it, too.
⇒ Colon Cancer
Colorectal cancer (also known as colon cancer, rectal cancer or bowel cancer) is the development of cancer in the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). It is due to the abnormal growth of cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. Rectal cancer is cancer of the last several inches of the colon. Most colorectal cancers are due to lifestyle factors and increasing age, with only a small number of cases due to underlying genetic disorders.
⇒ Lung Cancer
Lung cancer, also known as carcinoma of the lung or pulmonary carcinoma, is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. If left untreated, this growth can spread beyond the lung by process of metastasis into nearby tissue or other parts of the body. Most cancers that start in the lung, known as primary lung cancers, are carcinomas that derive from epithelial cells. Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States, among both men and women.
⇒ Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer that occurs in a man’s prostate — a small walnut-shaped gland that produces the seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in men. Prostate cancer usually grows slowly and initially remains confined to the prostate gland, where it may not cause serious harm. While some types of prostate cancer grow slowly and may need minimal or no treatment, other types are aggressive and can spread quickly.

1 thought on “Cancer Resource Center”